Tantrum Talk: Understanding and Managing Meltdowns in Young Children
Tantrums are a normal part of child development, but they can be challenging for parents and caregivers to navigate. Young children often lack the vocabulary and emotional regulation skills to express their feelings effectively, leading to outbursts of frustration and anger. Understanding the causes of tantrums and developing effective strategies to manage them is crucial for promoting healthy emotional development in children. In this article, we will explore the world of tantrums, discussing their causes, signs, and management techniques.
Understanding Tantrums
Tantrums are intense emotional outbursts that can manifest in various ways, including screaming, crying, throwing toys, or physical aggression.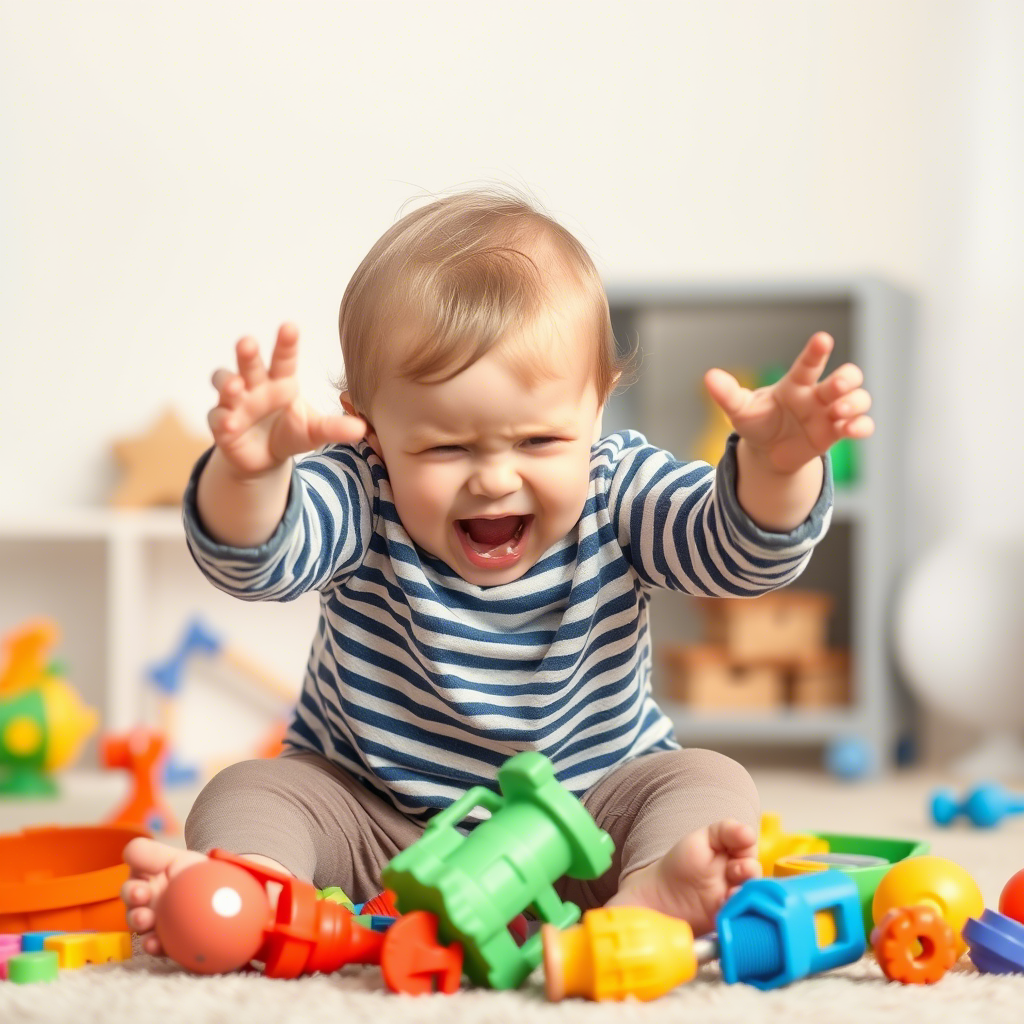  Research suggests that tantrums are a normal part of child development, with most children experiencing them between the ages of 1 and 3 years.
Research suggests that tantrums are a normal part of child development, with most children experiencing them between the ages of 1 and 3 years.
- Tantrums can be triggered by a range of factors, including frustration, tiredness, hunger, and overstimulation.
- Children may become overwhelmed by their emotions, leading to a loss of control and a tantrum.
- Tantrums can also be a way for children to communicate their needs and wants to caregivers.
Identifying the Causes of Tantrums
Identifying the underlying causes of tantrums is essential for developing effective management strategies. Some common causes of tantrums include:
- Frustration: Children may become frustrated when they are unable to accomplish a task or achieve a goal.
- Tiredness and hunger: Children who are tired or hungry may become irritable and prone to tantrums.
- Overstimulation: Too many stimuli, such as loud noises or bright lights, can overwhelm children and trigger a tantrum.
Recognizing the Signs of an Impending Tantrum
Being able to recognize the signs of an impending tantrum can help caregivers intervene early and prevent the situation from escalating. Some common signs include:
- Changes in behavior: Children may become restless, agitated, or withdrawn before a tantrum.
- Emotional cues: Children may exhibit emotional cues such as whining, complaining, or becoming easily annoyed.
- Physical signs: Children may display physical signs such as clenching their fists, tensing their muscles, or stomping their feet.
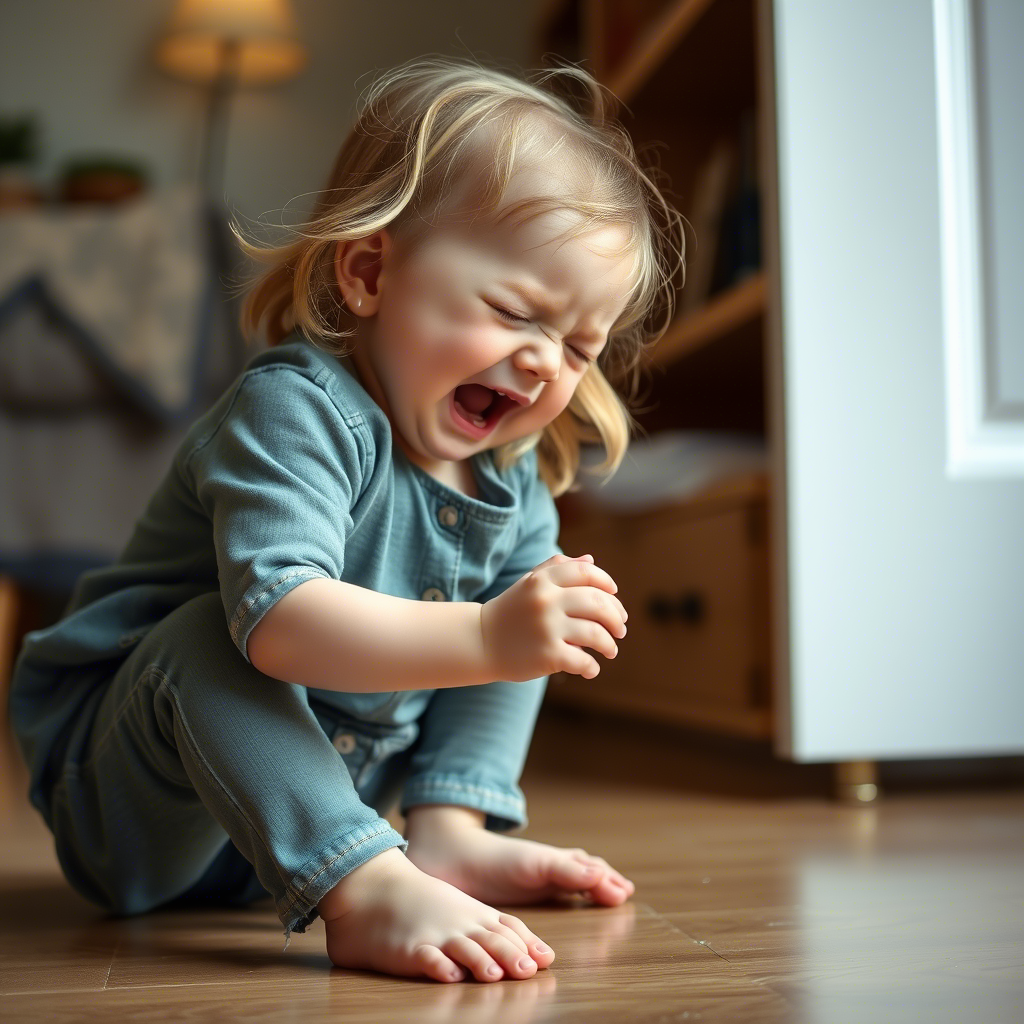

Managing Tantrums Effectively
Managing tantrums effectively requires a combination of empathy, patience, and consistency. Some strategies that caregivers can use include:
- Staying calm: Caregivers should remain calm and composed when dealing with a tantrum, as this can help to de-escalate the situation.
- Validating emotions: Acknowledging and validating a child’s emotions can help them feel heard and understood.
- Offering choices: Providing children with choices can help them feel more in control and reduce the likelihood of tantrums.
For more information on dressing your child for comfort during tantrums, consider checking out our collection of comfortable clothing, such as our boys’ coat, which can help keep your child warm and cozy.
Preventing Tantrums
Preventing tantrums is often more effective than trying to manage them after they occur. Some strategies that caregivers can use to prevent tantrums include:
- Establishing a routine: Establishing a daily routine can help children feel more secure and reduce the likelihood of tantrums.
- Encouraging communication: Encouraging children to communicate their needs and wants effectively can help reduce frustration and tantrums.
- Providing a calm environment: Creating a calm and peaceful environment can help reduce overstimulation and prevent tantrums.

You can also explore our girls’ clothing section for more comfortable and stylish options for your child.
Conclusion
Tantrums are a normal part of child development, but they can be challenging for parents and caregivers to navigate. By understanding the causes of tantrums, recognizing the signs of an impending tantrum, and developing effective management strategies, caregivers can help promote healthy emotional development in children. By staying calm, validating emotions, and offering choices, caregivers can help children develop the skills they need to regulate their emotions and manage stress effectively. With patience, consistency, and empathy, caregivers can help children navigate the challenges of tantrums and develop into emotionally resilient individuals.
Comments